





Star Homes, Tanzania
Main objectives of the project
Addressing the severe housing and health challenges in rural Tanzania, the Star Homes Project delivers 110 innovative, low-cost homes designed to reduce disease and improve living conditions. The project's emphasis on sustainability is evident through its use of energy-efficient materials and designs, significantly lowering embodied carbon and construction costs. By sourcing all materials and labor locally, the project strengthens community ties and builds local capacity. This interdisciplinary effort not only enhances the health and well-being of families but also serves as a model for sustainable development in similar regions.
Date
- 2024: Implementation
Stakeholders
- Architect: ingvartsen
- Ifakara Health Institute
- Mahidol Oxford Research Unit
- University of the Philippines – Manila
- London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
- Durham University
- CSK
Location
Country/Region: Mtwara, United Republic of Tanzania
Description
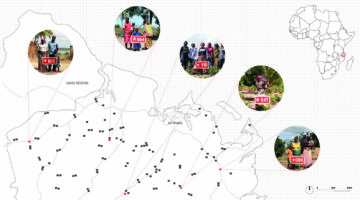
The Star Homes Project has been under development for over a decade, aiming to create novel, low-cost, comfortable, and insect-proof housing to improve health in rural areas of Sub-Saharan Africa. This initiative involves constructing 110 identical, single-family "Star Homes" across 60 different villages in Mtwara, one of Tanzania's most underdeveloped regions with high incidences of malaria, respiratory tract infections, and diarrhea. These houses are part of a trial designed to provide robust data on whether improved housing can enhance family health.
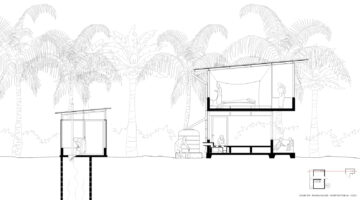
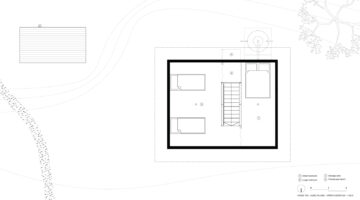
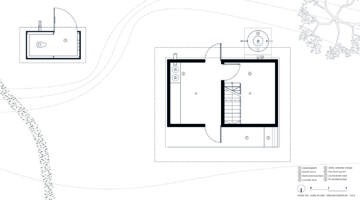
Both upgraded and traditional house styles in Sub-Saharan Africa seem to predispose residents to vector-borne, enteric, and respiratory diseases. Unlike most rural Tanzanian housing, the prototype house is two stories high, reducing the area of the foundation and roof, which are typically the most expensive and material-intensive components. This design approach optimizes resource use, reducing embodied energy and construction costs. The prefabricated light gauge steel (LGS) frame can be manufactured and erected in under three days; walls are solid but hollow, with two thin layers of cement render on wire mesh. The house features passive cooling, solar lights, USB chargers, and rainwater collection, resulting in a home that uses 70% less concrete than typical concrete block designs and has 37% less embodied carbon.
The prototype windows are screened with strong netting instead of glass, keeping indoor temperatures approximately 2.5 degrees lower than comparable local houses. Thick walls absorb heat during the day and radiate it at night, deterring the use of bed nets and increasing malaria risk. Ground-level bedrooms have higher mosquito densities, raising the risk of vector-borne infections. Cooking on open fires within poorly ventilated spaces can lead to respiratory health issues, especially for women and children. Compacted earth surfaces are hard to clean, and combined with open pit latrines, inadequate water supply, and minimal sanitation, they leave families vulnerable to diarrhea and other enteric infections.
These health issues are most severe in rural regions like Mtwara, where access to public health services is limited. After completing the construction of all 110 Star Homes in June 2021, families moved in and began participating in a trial to monitor children under 13 years old for episodes of malaria, acute respiratory infections, and diarrhea over three years. A team of architects, entomologists, and social scientists will evaluate the house design's performance and acceptability using in-depth interviews, focus group discussions, house walk-throughs, and surveys. Light traps will be used to collect mosquitoes and flies in both the Star Homes and control homes to measure the number of malaria-carrying mosquitoes entering the houses.
The Star Homes project also aims to build capacity and sustainable communities in some of the world's poorest areas by providing affordable housing and teaching new construction skills. Each house and latrine costs between $6000 and $8000 to build and can be constructed in under four weeks. Occupants receive electricity and water throughout the house's 30-year predicted lifespan, with no operational or maintenance costs. This saves time and resources, which can be used to strengthen rural communities and lift families out of poverty. All components and labor are sourced from within Tanzania, enhancing local construction capacity.
Designed by an interdisciplinary team of architects, public health specialists, and entomologists, the Star Home incorporates various design interventions to improve family health. A detailed selection process was undertaken to choose the recipients and locations for the Star Homes. In 2019, before construction began, a survey of rural villages in Mtwara was conducted. Households wanting to participate and meeting the study inclusion criteria (such as having children under 13 years old) could enter a lottery to win a Star Home built on their land. The lottery was conducted openly and transparently to select the recipients. The study is expected to be completed by 2024.








