



Las Carolinas-Entrepatios, Madrid
Main objectives of the project
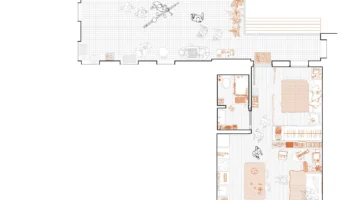
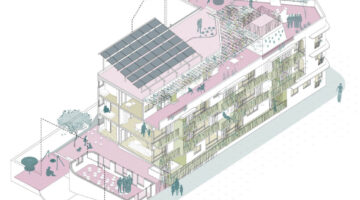
Las Carolinas-Entrepatios is the first ecological building with right of use in Spain that has been built between the centre of Madrid and the suburbs. It is a cohousing project, which means that it is the neighbours, members of the cooperative, who, through a participatory decision-making process, have decided on everything from the ecological materials to be used in the construction of the building to what part of the budget will be allocated to the insulation of the building and the type of air conditioning, among other things. Communal spaces make up 15% of the building: a communal courtyard; a room that serves as a children’s play area and as a space for weekly food distribution; a garage with mainly bicycles; a room dedicated to housing a large cistern where rainwater is collected, treated and used for toilets and gardening, by drip; a workshop room where neighbours work with their hands; a communal laundry; and a rooftop dedicated to adult leisure. The child population accounts for almost half of the total, some twenty children between the ages of two and twelve. Las Carolinas cooperative is made up of the fifty-three people who live in its seventeen dwellings. Depending on the size of their dwelling, they have paid between 40,000 and 50,000 euros as a down payment, an amount that will be returned if they leave the cooperative and replaced by those who move in. The ownership of the building remains in the hands of the cooperative and its members use the homes, but never own them.
Date
- 2020: Construction
- 2016: En proceso
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Entrepatios
- Architect: Lógica’Eco
- Architect: TécnicaEco
- Architect: sAtt
Location
City: Madrid
Country/Region: Madrid, Spain
Description
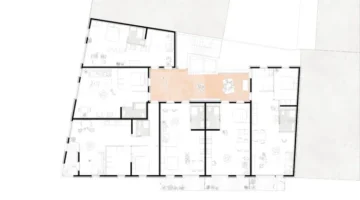
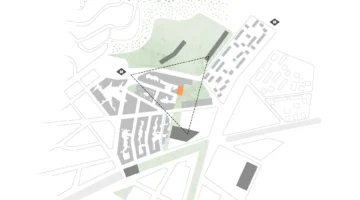
A few meters from the Manzanares River, in the neighborhood of Carolinas, in Orcasur (Usera), stands the first right-to-use collaborative housing building in the city of Madrid. This project, focused on environmental and community sustainability, has been conceived as a building with its own energy production and a very low energy demand, housing a community based on mutual support. The Las Carolinas development consists of 17 homes, inhabited by 32 adults and 20 children.
Usera, where this innovative building is located, is a peripheral municipality of Madrid that has faced social challenges, including difficulties of access to housing. Emerging from an active neighborhood movement, this project represents a radical, anti-speculative and accessible solution that integrates with the local community. In contrast to the dynamics of marginalization and privatization that have affected the neighborhood, the Entrepatios initiative aims to create inclusive spaces that strengthen the community fabric.
The system used involves a group of people forming a cooperative, which acquires the land and constructs the building. However, the residents do not own the land; instead, they only have the right to use the building as part of the cooperative. This approach prioritizes the use value of the building over land value speculation, offering a solution against gentrification and dispossession.
Since the acquisition of the site in 2016, the cooperative has navigated various forms of participation in the management of the process, with the collaboration of Lógica'Eco for technical aspects and the architectural design by the sAtt studio and TécnicaEco. Funding came from ethical banking and donations. The building, located on an elongated south-facing site, consists of 17 apartments with access through an outdoor corrala, which serves as a circulation and meeting space. Common spaces include first floor and attic space for various community activities, as well as a small workshop in the basement and a common laundry room.
In keeping with its commitment to climate change mitigation and resident comfort, the building prioritizes energy efficiency and comfort, especially in summer, through quality insulation and renewable energy generation. The garden is drip-fed, a rainwater cistern is provided for water savings, and the materials used prevent the release of volatile organic materials. A wooden structure is used. In order to have clean air, we will have a double-flow controlled mechanical ventilation system, which will prevent pollutants from entering from the outside thanks to a filter. This initiative seeks to reduce energy demand and promote a more sustainable lifestyle in a city increasingly affected by heat. The project has been certified with ECOMETRO and has been designed with high energy efficiency standards, incorporating renewable technologies such as solar panels on the roof.
The Entrepatios building is proof of the possibility of housing that is free from speculation, resilient to climate change, and fosters cooperative and communal living in a vulnerable neighborhood of a large metropolis.