Caserne de Reuilly
Main objectives of the project
The Caserne de Reuilly stands as a flagship urban renewal endeavor aimed at providing accessible housing solutions in the heart of Paris. As an integral component of the city's sustainable development strategy, this initiative marks a significant shift in repurposing former military infrastructure for social good. Under the joint efforts of the public housing entity Paris Habitat, municipal authorities, the State, and local stakeholders, the barracks underwent a comprehensive revitalization process, prioritizing circularity principles while preserving its historical significance. Amidst the backdrop of Paris' dense urban landscape, the transformation of Reuilly has not only addressed the shortage of affordable housing but also cultivated a diverse and inclusive community. Now encompassing a mix of affordable residences, student accommodations, childcare facilities, green spaces, and commercial establishments, the area has been transformed from a vacant lot into a thriving neighborhood, embodying the city's commitment to sustainable urban development.
Date
- 2019: Construction
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Paris Habitat
- Architect: NP2F
- Architect: Lin Architects Urbanists
- Architect: Mir Architectes
- Architect: Charles-Henri Tachon
- Architect: LACROIX CHESSEX
Location
City: Paris
Country/Region: France, Paris
Description
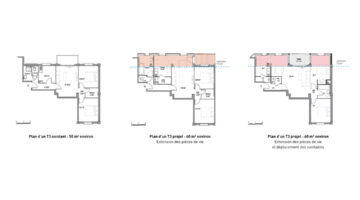
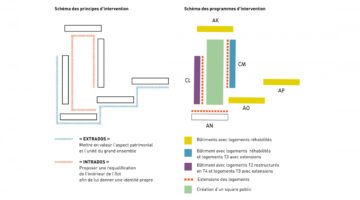
The history of the Caserne de Reuilly dates back to the 17th century, but by the early 21st century, the barracks were in dire need of refurbishment. Consequently, the city of Paris acquired the land from the Defense Ministry with the aim of rejuvenating the area. Collaborating with Paris Habitat, the site underwent a transformation into a new neighborhood featuring social housing, university residences, and commercial zones. The overarching goal was to preserve the historical character while introducing new spaces, fostering a diverse and mixed-use community. In total, the development comprises 582 housing units.
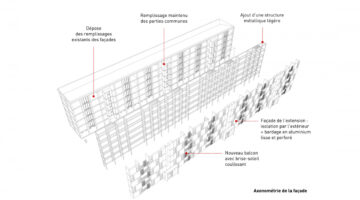
Paris Habitat demonstrated pioneering efforts by integrating the reuse of materials into the project. For instance, lighting fixtures, slates, and paving stones from the barracks were repurposed on-site. In addition to refurbishing the old barracks, new buildings were erected, such as those along Diderot Boulevard, which harmoniously blend with the existing architecture. These buildings incorporate 79 dwellings, a childcare facility, a public parking lot, and commercial spaces. The architectural design responds directly to the surrounding context while embracing contemporary elements, contributing to the coherence of the neighborhood. Addressing the space between the fire station, Reuilly barracks, and the new construction was a key challenge. The proposed structure aims to reconcile various geometries, resulting in a complex yet cohesive architectural form characterized by terraces and indentations. The inclusion of a square between the buildings encourages social interaction, while the lower volume's roof serves as a playground for the childcare facility, fostering a vibrant community atmosphere.
Similarly, the residential building known as plot B1, comprising 22 housing units, serves as an entry point to the barracks complex. Its colorful façade distinguishes it from the rest of the development while maintaining overall harmony, serving as a visible and inviting gateway to the barracks.
In essence, the new complex exemplifies how to create affordable housing while preserving public ownership, employing high-quality architecture, and embracing a variety of housing typologies to nurture a diverse and inclusive community.