Johannesburg Housing Company
Main objectives of the project
When addressing informal settlements and the relocation of their residents, the common solution often involves outskirts due to their affordability. Typically, a large proportion of slum dwellers gravitate towards the outskirts of cities. However, Johannesburg has adopted a different approach. In efforts to rejuvenate its downtown area, the city has embraced an alternative strategy. Through the utilization of a non-profit institution, Johannesburg has implemented social housing initiatives within its city center. By repurposing abandoned or deteriorating buildings, the city has not only revitalized its downtown core but also provided much-needed social housing options.
Date
- 1995: Implementation
Stakeholders
- SHRA
- Promotor: JHC
Location
Country/Region: Johannesburg, South Africa
Description
In South Africa, a significant portion of tenants reside in informal settlements, with over 400,000 housing units constructed on unauthorized land lacking basic services and vulnerable to environmental hazards like floods and fires. Between 2001 and 2011, the number of shacks erected in the backyards of existing dwellings surged by 55%, totaling more than 700,000 units. Despite the existence of the Social Housing Policy since 1994, the establishment of the regulatory authority (SHRA) in 2010 marked notable progress. The Minister of Human Settlements pledged the delivery of 1.5 million new housing opportunities by 2019.
Social housing projects are financed through a blend of government funds, debt, and up to 10% from for-profit private capital. The national government, via the SHRA, subsidizes up to 65% of capital costs and allows subsidized units for tenants meeting specific monthly family income thresholds. These subsidized units must constitute between 30% and 70% of all mixed projects.
Investment opportunities include the Social Housing Institution (SHI) model, where non-profit entities or owners undertake projects inclusive of social housing. Currently, around 83 SHIs have been established, delivering approximately 33,000 units nationwide. However, while the number of institutions is on the rise, the rate of unit development hasn't matched, leading to financial challenges for many. Only six out of the 83 institutions are financially stable, with an additional 25 potentially viable.
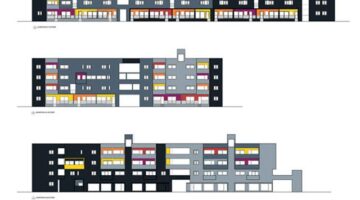
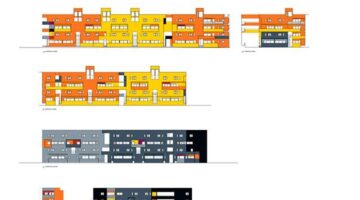
In Johannesburg, two SHIs have demonstrated remarkable success. One such entity is the Johannesburg Housing Company (JHC), founded in 1995, which has pioneered an innovative affordable housing model with efficient building management and exemplary customer service. It has facilitated the development of over 4,293 rental housing units, providing homes for more than 19,478 individuals. JHC's efforts have played a pivotal role in revitalizing downtown Johannesburg, transforming dilapidated or abandoned buildings into modern architecture units. The company utilizes two components of the rental housing policy: urban restructuring zones declaration and the Inner City Property Scheme (ICPS), formerly known as the Bad Building Program.
Initial funding provided to JHC enabled it to establish a solid capital base necessary for large-scale social housing development in the downtown area. By the late 2000s, JHC had a portfolio comprising nine renovated buildings and two new construction projects. The organization's cost management strategy ensures each building covers its operating costs, including interest on operating income.
Contrary to traditional urban regeneration strategies focused solely on economic growth, JHC's approach emphasizes building improvements, renovations, and new constructions to increase the city's housing stock by approximately 10% while rejuvenating rundown structures to provide affordable rents and decent housing. However, the future of social rental housing faces challenges, particularly regarding the diminishing availability of affordable land in restructuring zones.