Llargavista observatory
Main objectives of the project
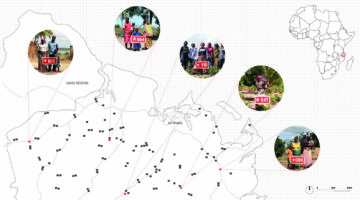
The Llargavista observatory consists of a website and an interactive map showing all registered cooperative housing initiatives in Catalonia (Spain), providing detailed information on each project obtained through questionnaires and interviews. Its objective is to disseminate the model and its evolution to all citizens in an accessible and understandable way.
Date
- 2020: Implementation
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Sostre Cívic
- Coòpolis
- Xarxa d'Economia Solidària
- iLabSo
- Risell
Location
City:
Country/Region: Barcelona, Spain
Description
"Llargavista" means "long-term" in Catalan. This name is not accidental. The observatory seeks to map all cooperative housing in Catalonia, a nation within Spain, with the goal to make it a long-term solution for the housing crisis. Catalonia (and specifically Barcelona, its capital) has been a pioneer in a specific type of cooperative housing with “the right to use”. That is to say, the administration cedes the land in surface right to a cooperative, which constructs the building. After the period agreed with the cooperative, the building becomes public property. Thus, the cooperative never owns the land, but it does own the building for a certain agreed period of time. During that time, the people living in the housing must meet the requirements for access to public social housing and, in exchange for an entrance fee, be cooperative members. If they wish to leave the housing, they leave their share of the cooperative to whoever enters. The observatory monitors these initiatives.
This is an initiative promoted by Sostre Cívic, with the collaboration of Risell and iLabSo and the participation of the housing sector of the Xarxa d'Economia Solidària (XES) and the Cercle de transició ecosocial de Coòpolis. It is supported and financed by the General Directorate of Social Economy of the Generalitat de Catalunya and the Barcelona City Council. With the creation of this initiative, the aim is to observe the state and evolution of cooperative housing in cession of use throughout the country. At the same time, this tool is built with a long-term vision, to consolidate and grow cooperative housing as a transformative and non-speculative model of housing access and tenure.
The main objective is to carry out a quantitative and qualitative analysis of the cooperative housing sector in transfer of use, both of information related to the people and cohabitation units that participate, as well as the characteristics of the building or the project, and other elements of interest related to the project, such as economic and financial information or its social impact. This information, systematized and sustained over time, can be of interest to the cooperative housing sector, the academic world, public administrations and the media, among other agents. In addition, it aims to show the information in an accessible and understandable way in order to disseminate the model, the projects and their evolution to all citizens with a clearly informative function.
The main product of the observatory is a website and an interactive map that it incorporates, which shows all the registered cooperative housing initiatives in cession of use, with information on each project. The data is obtained through questionnaires answered by groups and projects throughout the country and through interviews with groups and various agents.