Transformation of 530 dwellings - Grand Parc Bordeaux
Main objectives of the project
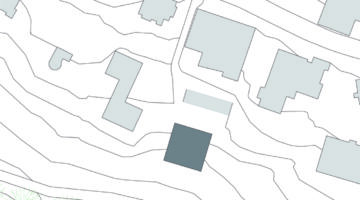
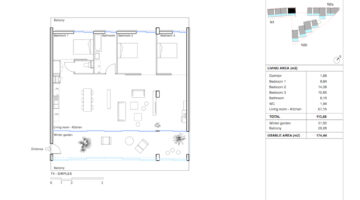
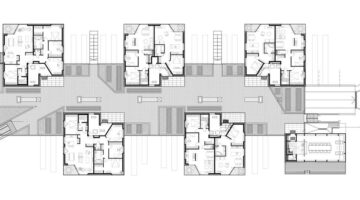
As the recipient of the 2019 EU Mies van der Rohe Award, this project involved the refurbishment of three social housing buildings comprising 530 units in Bordeaux, France. Originally constructed in the early 1960s, the need for renovation arose after the possibility of demolition was dismissed. Remarkably, the transformation of these dwellings occurred while residents continued to occupy them. A key aspect of the renovation involved extending the existing space by adding a winter gardens and balconies accessible from every room, akin to a traditional house layout. This expansion not only broadened the usable space and mobility within the buildings but also redefined the quality of housing offered while improving the energy efficiency of the building envelope. This project serves as a compelling example of forward-thinking, responsible housing solutions for the future.
Date
- 2017: Construction
- 2019: Ganador
Stakeholders
- Promotor: AQUITANIS
- Architect: Christophe Hutin Architecture
- Architect: Frédéric Druot Architecture
- Architect: Lacaton & Vassal architectes
Location
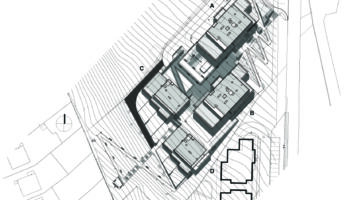
City: Bordeaux
Country/Region: Bordeaux, France
Description
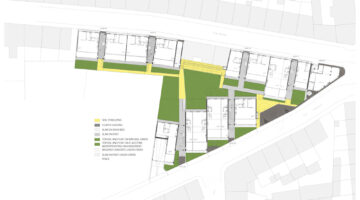
This project presents a bold approach to challenging the existing European housing stock from the post-war era, achieving remarkable results with minimal resources. Rather than opting for demolition, which consumes significant energy, the client recognized and endorsed the benefits of transforming three existing buildings. Through this initiative, social housing, often criticized for its built heritage, serves as a model for relevant and cost-effective transformation, turning perceived deficiencies into generous, inviting, and efficient dwellings that redefine typologies, living conditions, comfort, and aesthetics, thereby enhancing the urban residential landscape.
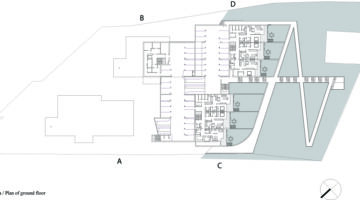
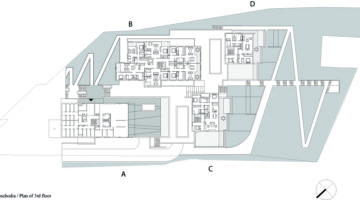
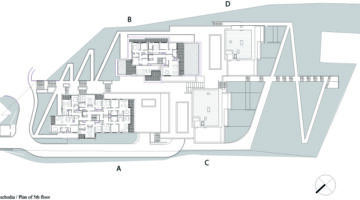
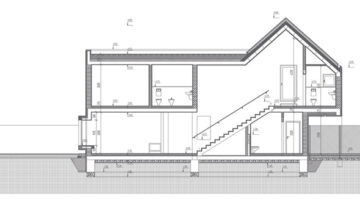
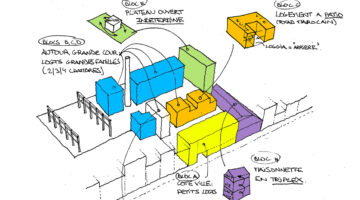
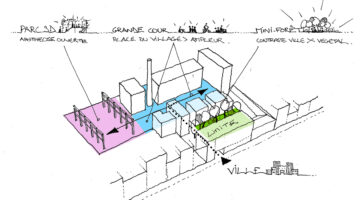
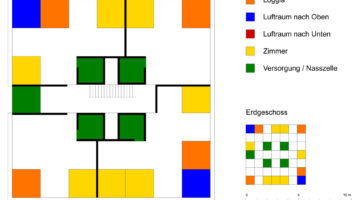
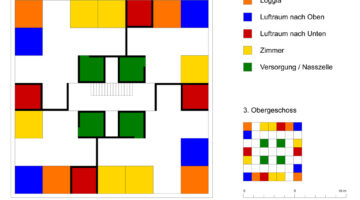
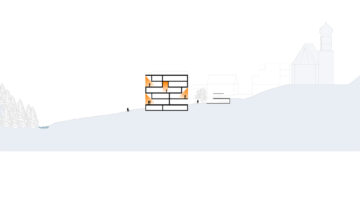
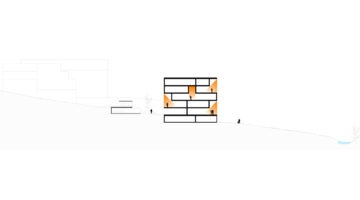
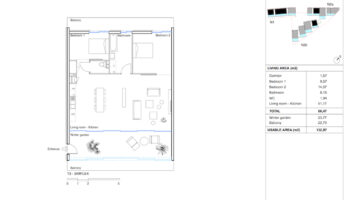
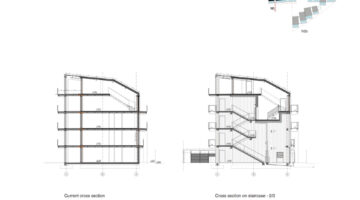
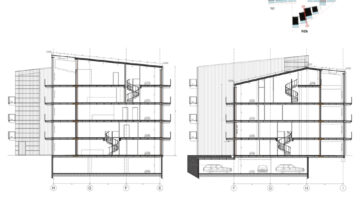
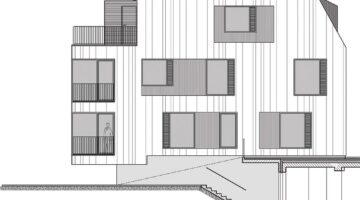
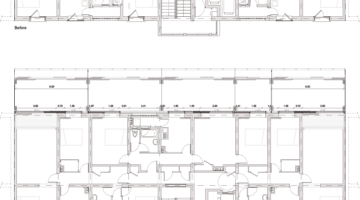
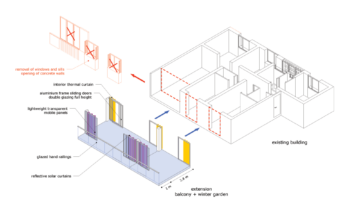
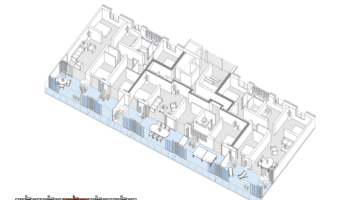
The transformation imbues all dwellings with new spatial qualities and living standards by meticulously assessing existing strengths to preserve and identifying areas for enhancement. The addition of expansive winter gardens and balconies to each apartment offers increased space, natural light, usability, and panoramic views. Small existing windows are replaced with large glazed sliding doors opening onto the winter gardens. Technical upgrades include renovations to bathrooms, electrical systems, and the replacement of two former elevators with a larger, more efficient one in each staircase. New access halls and improved front gardens enhance the overall environment. Throughout the construction process, all families remained in their dwellings, with no rent increase post-transformation.
The project, executed with inhabitants in residence, avoids structural interventions such as changes to stairs or floors, opting instead for additions and extensions designed for full utilization. Internally, only facility refurbishments and finishings were undertaken. The 3.80-meter extensions expand usable space and mobility, seamlessly connecting rooms to the winter gardens, akin to private semi-outdoor spaces found in houses. The energy efficiency of the building envelope is significantly enhanced by these winter gardens, serving as passive solar collectors. Focusing on economy, the budget prioritizes extensions, crucial for substantial and sustainable improvements in dwelling quality, while overall transformation costs remain within budget parameters, aligning with typical expenses for basic facade renovations, insulation, and facilities.
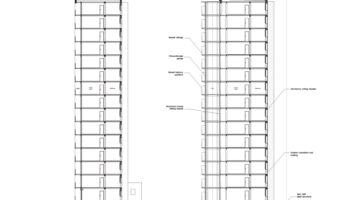
Construction materials and methods were selected to optimize efficiency and minimize disruption. Concrete was exclusively used for foundations, with concrete window sills removed to facilitate floor-to-ceiling openings for double-glazed sliding doors. Thermal curtains enhance interior insulation. Lightweight facades composed of transparent, corrugated polycarbonate panels and aluminum-framed glass, equipped with reflective solar curtains, provide exterior insulation. Glazed handrails line the balconies.
To expedite construction, prefabricated modules were employed, erected like scaffolding in front of the buildings. Precast slabs and columns were transported to the site and assembled into a freestanding structure using a crane. Efficient planning and scheduling allowed for a swift transformation, completing each apartment within 12-16 days: half a day for laying concrete slabs, two days for adapting the old facade, two days for installing the new facade, and 8-12 days for interior renovations.