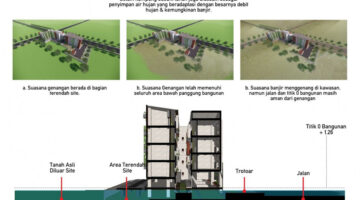
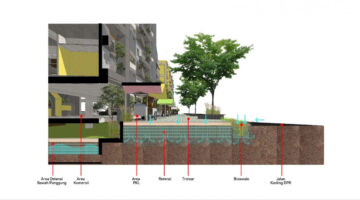
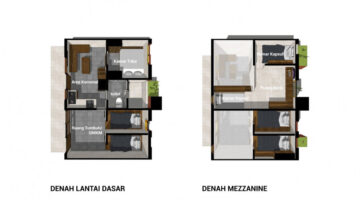
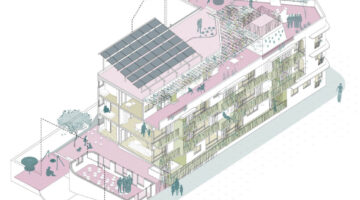
Ixtepec Reconstruction
Main objectives of the project
In September 2017, Oaxaca, Mexico, experienced its most devastating earthquake in history, severely damaging the traditionally constructed homes of indigenous communities. However, the intervention of the local NGO Cooperación Comunitaria (CC) revolutionized the situation, rallying the community to construct homes capable of withstanding earthquakes while utilizing traditional techniques suited to the local climate and culture. This initiative stood in stark contrast to the approach of state and federal governments, which aimed for a rapid, market-driven reconstruction. Their plan involved demolishing affected homes and providing a 120,000-peso card to construct standardized prototypes, disregarding the needs of the population, local organization, and the cultural and climatic context of the region. In response, CC has worked alongside affected communities, supporting processes of social reconstruction, fostering solidarity and self-organization, and respecting their cultural traditions and way of life.
Date
- 2017: Construction
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Cooperación Comunitaria
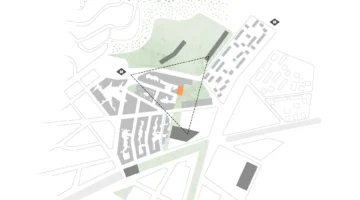
Location
Country/Region: Mexico
Description
In 2017, the devastating earthquake in Oaxaca struck the indigenous community of Ixtepecano, prompting the municipal government to initiate demolition, replacing traditional architectural heritage with modern, inadequate housing. However, the intervention of local NGO Cooperación Comunitaria A.C. brought about a significant transformation.
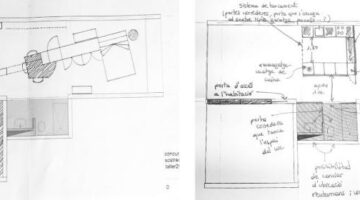
The initiative began within the community itself when the Ixtepecano Committee, a local organization, reached out to Cooperación Comunitaria A.C. to aid in rebuilding homes. CC conducted thorough assessments of the damage and vulnerability of families, including mapping exercises. Through assemblies and meetings, a reconstruction model was collaboratively developed with the families. As part of the technical assistance and social support process, CC revived traditional construction methods with the communities, emphasizing the use of local materials to reduce ecological impact and make self-construction of housing feasible. Traditional housing styles such as Bajareque, Adobe, and brick and rope were recovered and reinforced to withstand earthquakes and strong winds without compromising cultural and climatic suitability.
Recognizing the importance of economic recovery alongside housing reconstruction, traditional ovens and kitchens were integrated into the rebuilding process to revive local women's livelihoods. An Arts and Trades Centre was established to train individuals in traditional building techniques for kitchen construction. Additionally, local maize varieties were reintroduced for staple totopos production, while workshops on construction skills, disaster risk management, and natural resource utilization were conducted. Notably, 107 women have revitalized their businesses through the restoration of 196 traditional ovens and kitchens, contributing to household economic recovery. Model kitchen proposals developed in community design workshops, education on natural resource management for 247 individuals, and training for 73 builders on reinforcement techniques further enhanced community resilience.
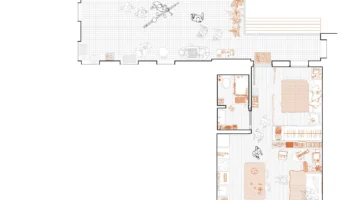
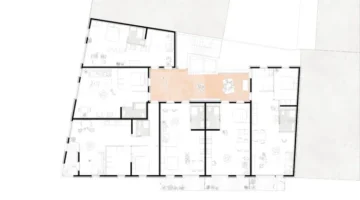
The project has restored and reinforced 58 traditional houses, built 22 new reinforced houses, reinforced 90 kitchens with the bajareque cerén construction system, constructed 256 comixcales and 27 bread ovens, along with 2 community centers and 2 dry toilets. This reconstruction process underscores the effectiveness and necessity of traditional collective work and mutual support approaches. Activities reinforcing community organization, such as integral community diagnosis and participative design, along with technical knowledge transmission and training on risk management and housing rights, are integral parts of the project. Continuous evaluation of housing conditions, usage, and maintenance ensures sustainability.
This project exemplifies how community empowerment can counter government displacement and update traditional structures to meet 21st-century needs, emphasizing resilience. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of cooperative and communal economic structures alongside housing restoration to ensure affordability.