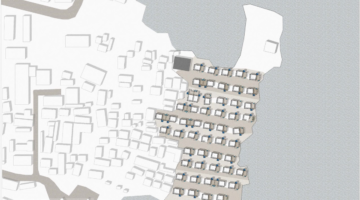

Reconstruction plan for Precious Seeds, Oworonshoki
Main objectives of the project
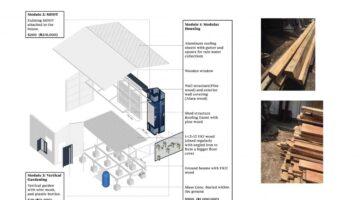
The reconstruction scheme for Precious Seed in Oworonshoki focuses on simplicity, affordability, and modularity, promoting sustainable community rebuilding. With features like a one-room house with a veranda, vertical farming elements, and Mobile Dry Diversion Toilets (MDDT), the project emphasizes protection, efficient use of limited resources, and community empowerment. The large roofs provide essential shelter, creating a blend of private and public spaces. The initiative, costing around 1,120 US$ per house, fosters community cohesion, particularly through the formation of a women's group to lead the reconstruction based on local building codes, highlighting values of resilience, inclusivity, and strategic, incremental development.
Date
- 2024: En proceso
Stakeholders
- Architect: FABULOUS URBAN
Location
Country/Region: Lagos
Description
The reconstruction scheme for Precious Seed, a community in the Oworonshoki neighborhood severely impacted by state and local king-led demolitions, is marked by its simple, affordable, and modular design at all levels.
A one-room house with a veranda, vertical farming elements, and the well-tested Mobile Dry Diversion Toilet (MDDT) was developed. These houses can be combined into larger units depending on funding availability and plot size.
A key feature is the large roof, offering protection from the sun and rain in Lagos' year-round hot and humid climate. The roofs and stoops together create a graduated yet flowing space between private and public areas, maximizing the use of limited resources, including poverty constraints and small plot sizes.
Each house can be constructed for approximately 900 US$, the MDDT for about 200 US$, and the vertical farming mesh for 20 US$.
In 2024, the next steps involve establishing a strong, cohesive women's group dedicated to developing and implementing a strategic plan for community rebuilding, based on the guidelines from the Oworonshoki Local Building Code Project. Initially, a prototype house will be built, serving as a capacity-building tool for women. As the women's group becomes more established and additional funds are secured, the community will be incrementally reconstructed.