



Tinggården, Denmark
Main objectives of the project
Since its construction in 1978, Tinggården has stood as the archetype of low-rise, high-density residential architecture in Denmark. Situated on open land in the town of Herfølge, Tinggården represents a highly successful non-profit housing experiment that utilized architecture to reestablish residents' democracy within the local community. It is renowned as one of the pioneering cohousing experiments globally.
Date
- 1978: Construction
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Danish Building Research Institute
- Architect: Vandkunsten Architects
Location
Country/Region: Denmark
Description
In the 1960s, a group of architects and families in Denmark who sought more interaction with their neighbours initiated the cohousing movement, characterized by private houses grouped around common spaces and facilities. Tinggården was one of the first projects to implement these cohousing theories.
In 1971, the Danish Building Research Institute (SBI) held a competition on alternative housing forms. This competition presented an opportunity to demonstrate flexible, human-scaled architecture as a radical contrast to the technocratic high-rise developments and the perceived monotony of suburban single-family homes. Vandkunsten Architects won the competition with a proposal that emphasized community and aimed to give residents real influence over both the architectural design and their ability to shape their lives and homes. This competition paved the way for the Tinggården housing experiment and led to the establishment of Vandkunsten Architects.
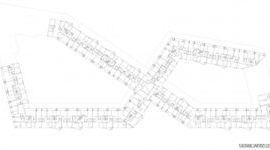
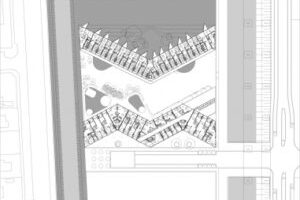
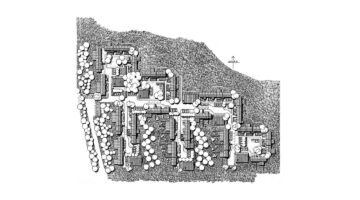
Tinggården was completed in 1978, originally consisting of 78 homes arranged into six family clusters, each with a communal building for shared meals and activities. Additionally, a large communal hall was built for all Tinggården residents. The development expanded in a second phase from 1983 to 1984, doubling the number of homes, a testament to its success.
Each cluster features its own community house, small squares, and gathering places. All homes have access to their social community and direct access to the surrounding landscape, which is fundamental to low-rise, high-density architecture. The architects chose shapes, colors, and timber cladding similar to the red and cream-colored Danish barns in the surrounding area.