





Tunkhel Village
Main objectives of the project
Mongolia, known for its fiercely independent nomadic herders, is undergoing urbanization, prompting urban dwellers to seek more communal solutions to address issues such as poverty and housing. In Tunkhel Village, ten impoverished families in a timber town embraced collective action, departing from the individualistic ethos, to collaboratively rebuild their deteriorating Soviet-era housing using energy-efficient methods. Their initiative not only transformed their living conditions but also influenced government housing policies.
Date
- 2009: Construction
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Tunkheliin Hugjil savings group
- Architect: Yagaanbandi
- Asian Coalition for Housing Rights (ACHR)
- Urban Development Resource Center (UDRC)
Location
Country/Region: Mongolia
Description
Tunkhel Village, nestled in Mandal District amidst the forest-clad mountains of north-central Mongolia and located 126 km from Ulaanbaatar along the railway line to Russia, sustains a population of approximately 3,721 individuals residing in 980 households. Despite the stunning natural scenery, the village grapples with multifaceted challenges. Formerly reliant on timber production as its primary industry, Tunkhel faced economic downturns following the closure of state-run lumber mills at the conclusion of Mongolia's socialist era. Consequently, unemployment surged to 60%, accompanied by escalating poverty, alcoholism, and social issues. Predominantly, residents inhabit unserviced ger areas characterized by unpaved, unlit roads strewn with uncollected refuse, prompting many to seek alternative livelihoods such as seasonal market gardening and livestock rearing. Presently, livestock outnumber humans by a ratio of ten to one in this settlement.
Since 2009, Tunkhel Village has witnessed the establishment of 17 community-managed savings groups, facilitated by the Urban Development Resource Center (UDRC), a non-governmental organization based in Ulaanbaatar. In April of that year, UDRC, in collaboration with the Asian Coalition for Community Action (ACCA) Program, initiated a comprehensive community upgrading initiative in Tunkhel. A joint committee, comprising representatives from community savings groups and local government entities, was instituted to oversee the project's execution. Subsequently, an agreement was formalized through a memorandum of understanding (MOU) and action plan, whereby the local government pledged office space for village-based ger (1) area development operations. The collaborative efforts between community groups and the local government culminated in the inauguration of the village's inaugural joint community development project—a wooden bridge spanning the river. This venture, funded entirely by the local government and staffed by community volunteers, addressed a longstanding infrastructure need within a mere two weeks of construction.
The success of this initial collective endeavor instigated a series of communal projects, including the establishment of children's playgrounds, implementation of waste-collection systems, inauguration of a community products shop, and renovation of a destitute widow's dilapidated dwelling. Emboldened by these accomplishments, the savings network proposed a housing project spearheaded by the Tunkheliin Hugjil savings group. This proposal, endorsed in August 2009, initially garnered the interest of all 16 households within the savings group, though ultimately, six families opted to pursue independent avenues, securing loans from the nascent community fund to acquire land and houses elsewhere. Over the ensuing three months, the remaining ten families collaborated to raze their antiquated residences and erect modern replacements.
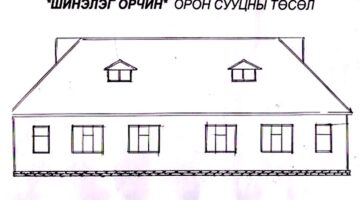
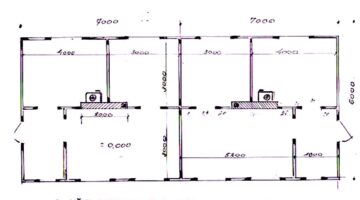
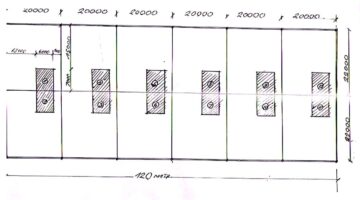
Each family procured a loan amounting to $3,750 (equivalent to 5 million tugrik) from the village-level revolving fund for house construction, bearing a 6% annual interest rate repayable over five years at a monthly installment of 110,000 tugrik (approximating US$83). In adherence to individual financial capabilities, repayment terms were collectively determined and contributions remitted into the community's bank account. Leveraging Mongolia's abundant land resources, the families availed themselves of their entitlement to 7,000 square meters of government-allocated land, thereby assuming ownership of their respective plots. The newly constructed single-story, semi-detached dwellings, designed by the residents, feature a three-room living area spanning 42 square meters. Crafted from locally sourced timber and incorporating energy-efficient innovations to mitigate winter heating expenses, these residences are interconnected to the village's central steam-heating system, modernized in 2019. Additionally, the houses share communal outdoor pit latrines and boast double-glazed windows and insulated galvanized iron roofing sheets conducive to weathering Mongolia's harsh winters. Salvaged construction materials from the former residences supplemented the predominantly new building supplies, ensuring cost-effectiveness in the project's execution.
In a departure from conventional practices prevalent in Mongolia's ger areas, where residents typically erect high fences surrounding their properties, the project participants opted for a unified, inviting perimeter fence encouraging openness and community engagement. Noteworthy solidarity was exhibited during World Habitat Day celebrations in 2009, drawing volunteers from across Mongolia to assist in constructing this inclusive enclosure, symbolizing support for the pioneering collective housing endeavor.
Following the project's culmination, the local government allocated a disused building to the savings network, repurposed as a community center. Utilizing residual project funds, the facility underwent renovations, evolving into a vibrant communal hub frequented for social gatherings, meetings, and commercial activities. The center offers diverse services ranging from hairstyling and watch repair to mobile phone and computer maintenance, augmenting its significance as a vital community asset.
(1) A Ger district represents a common type of residential area found in Mongolian settlements. These districts typically comprise parcels containing one or more standalone traditional mobile dwellings, known as gers (thus named after them), enclosed by wooden fences standing at a height of approximately two meters. In other regions, gers are commonly referred to as yurts.

