





Nemausus, Nîmes
Main objectives of the project
Nemausus is one of Jean Nouvel's most renowned social housing projects, created for the Délégation à l'aménagement du territoire et à l'action régionale of the Ville de Nîmes. The concept behind the building is straightforward: recognizing that there are no standard families with uniform needs and that affordability is essential for making housing accessible to all, an effective social housing project should be both flexible and cost-efficient. In the Nemausus complex, Jean Nouvel addressed these considerations by developing a construction system using prefabricated components, enabling rapid and systematic assembly. The industrial aesthetic of the exterior is mirrored inside, featuring rough concrete walls, aeronautical-style windows, metal staircases, and prefabricated panels that fit together like a Meccano set. This design approach creates a diverse range of dwellings—from studios and one-bedroom apartments to double-height units and three-bedroom triplexes—all benefiting from abundant natural light and excellent ventilation.
Date
- 1987: Construction
Stakeholders
- Promotor: Ville de Nîmes
- Architect: Jean Nouvel
Location
Country/Region: France, Nimes
Description
Nîmes is a French city located in the south near the Mediterranean Sea. The city's fame largely stems from its numerous Roman-era buildings, including amphitheaters and aqueducts. The area enjoys a favorable climate for much of the year, and its residents often utilize public spaces, spending significant time away from home. However, Nîmes also faces substantial needs for social housing.
The objective of the Nemausus housing project was to address the needs of a constantly evolving society and to construct low-cost housing. The core idea was to define what constitutes a good apartment, which, according to its architect Jean Nouvel, is simply an apartment as large as possible. A good apartment is flexible and capable of being adapted. It should be affordable in a democratic sense. And more importantly, takes into consideration the time factor: after some years, needs might change. So, the building must too.
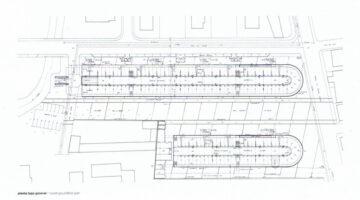
To optimize land use, the garage floor was designed to be semi-buried, adhering to a municipal ordinance and ensuring that the parking area does not obstruct views of the complex. Nouvel designed two elongated, almost parallel, boat-shaped buildings, with one being shorter than the other. Between them is a projected park and public space, which provides a sense of ownership to the residents. The design preserved two strips of trees from an old arboretum, running the length of the complex.
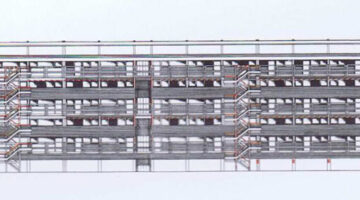
The two buildings feature semi-buried ground floor parking and three upper floors of apartments. The complex includes 114 housing units, ranging from simple apartments to duplexes and triplexes (such as studios and one-bedroom units with double-height ceilings). The total habitable area is 10,400 square meters, giving an average size of 91 square meters per dwelling, which is significantly larger than traditional social housing. Access to the buildings is via stairs located in the common area, separate from each building. Elevators are situated inside each building, centrally positioned. Horizontal corridors run the length of each building, covering all three floors. These corridors are designed as "high streets," wide enough for pedestrian and bicycle travel, and serve as communal spaces for neighbor interaction and housing expansion. On the opposite side facing the street and adjacent buildings, similar corridors function as private balconies for each unit. These passages expand the living space by opening the walls outward.
In Nemausus, the architect aimed to enhance the area by maximizing natural light and airflow, addressing issues that were previously neglected or undervalued. Currently, the buildings are home to a predominantly young population, with 80% of residents under 35 years old and the oldest being 51. Among the residents, 20% are unemployed, 3% are workers, 20% are employees, 31% are middle-class or educated individuals, 19% are students, and 7% belong to other categories.
To reduce costs, the building structure was designed to be practical and rational. The two buildings are supported by columns placed every five meters, surrounding the parking area. This design decision maintains visual continuity across both sides. The load-bearing walls, dividing each apartment, rest on these columns and are consistently spaced throughout the three floors. This modular approach creates uniformity across the building, allowing different apartment types to be easily configured.
The only deviation from the five-meter wall module is in the center of each building, where two walls are positioned closer together to accommodate the elevators. The stairs are detached from each building, featuring independent steel structures connected to the horizontal corridors by bridges.
The materials used in Nemausus contribute to its distinctive, radical appearance. To save costs, Nouvel utilized industrial materials and prefabricated components that are easy to replicate and assemble.

