



Kampung Susun Produktif Tumbuh Cakung, Jakarta
Main objectives of the project
In response to Jakarta's sinking crisis, Bukit Duri residents faced eviction in 2016. Deemed illegal, this sparked a movement led by Ciliwung Merdeka, empowering residents to demand their rights. The result? Kampung Susun—a cooperative where former residents manage their space, integrating living and economic activities, defying traditional public housing norms, and fostering community resilience and cohesion.
Date
- 2020: Construction
Stakeholders
- Constructor: PT. Jaya Konstruksi Manggala Pratama Tbk.
- Architect: STUDIO AKANOMA
- Promotor: Jakarta City Hall
- Promotor: Ciliwung Merdeka
Location
Country/Region: Indonesia, Jakarta
Description
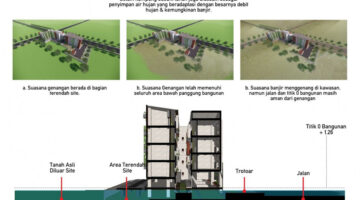
Jakarta is confronted with a significant threat: the city is sinking, resulting in more frequent floods and substantial portions of the city being submerged. The most vulnerable communities are bearing the brunt of this issue. In 2016, seventy families in Bukit Duri, Jakarta, were forcibly removed from their homes as part of efforts to address the city’s chronic flooding problems. However, the eviction was subsequently deemed illegal. In 2017, the State Administrative Court ruled that the eviction lacked legal justification and that the residents were entitled to compensation. Volunteers from the organization Ciliwung Merdeka collaborated with the residents, spanning from children to adults, to empower the community through various programs aimed at fostering solidarity and self-reliance. These initiatives encompassed educational programs for children, public health education, waste management, economic empowerment, art and culture education, disaster response and mitigation, as well as spatial planning and architecture. Additionally, they collectively advocated for government recognition that impoverished citizens deserved adequate living conditions and demonstrated that viable alternatives to eviction existed.
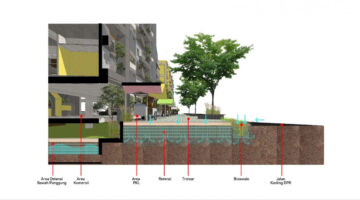
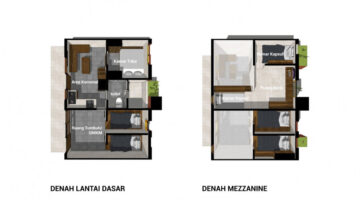
One such alternative materialized in the form of the Kampung Susun new residence and cooperative, where residents themselves assume responsibility for the neighborhood's upkeep. Tenants are not required to pay rent but are obligated to contribute a maintenance fee to the cooperative, which also has the capacity to provide residents with business capital. The design process began with identifying spaces tailored to the economic development needs of former Kampung Bukit Duri residents, the majority of whom are engaged in the informal business sector and own small enterprises. The design concept emulates the urban settlement model, featuring small houses with dedicated economic spaces, giving rise to the term "kampung susun." Notably, Kampung Susun stands out from Jakarta's conventional public housing projects, known as rusunawa, which typically lack provisions for business activities. Each residential unit in Kampung Susun encompasses both living and economic spaces, with communal areas on the ground floor enabling residents to engage in commerce. Additionally, residents have the opportunity to expand their living quarters vertically, facilitated by a mezzanine level within each unit.
Measuring 36 m2 in total, with 21 m2 designated for private use and 15 m2 allocated for business or workspace, each residential unit is designed to accommodate growth. This innovative approach to urban settlement, known as Kampung Susun Produktif Tumbuh, or growing, productive stacked kampong, addresses the challenges of densely populated urban environments and the limitations of traditional housing construction. Beyond serving as mere dwellings, Kampung Susun fosters a sense of community where residents can engage in economic activities and foster friendly interactions, recognizing the distinct characteristics of urban settlement inhabitants compared to those residing in the outskirts of the city.
The case is undoubtedly a resilient solution to an unprecedented climate problem. Bottom-up and from the community, it solves a huge challenge of obtaining public housing in an adverse context, promoting the productive economy of its residents.

